Photo by Jeremy Bezanger on Unsplash
Simple explanation : what is the difference between Intel , AMD & ARM processors ?
I've been working for some months on a Macbook M1, and i had to adapt in order to make some applications work on my machine, but i did not know very well the reason about that, so i decided to dig a new subject : Processors
Definition
What is a Processor ?
Also known as Central Processing Units (CPUs), a processor is a small chip that act as brains for computers and smartphones. The CPU is responsible for calculations, caching critical information for quick access, and more.
Manufacturers vs Architecture
Intel and AMD are manufacturers, but ARM processors are a type of architecture, and therefore they do not have only one manufacturer, so it's not really the point to compare them.
Intel
Intel is the most popular and well-known maker of processors.
Manufacturers like Dell, Apple, Samsung and HP all use Intel processors in their computers.
Intel processors are the most stable and offer the best all-round performance.
AMD
AMD is Intel’s biggest competitor, offering processors that are similar to Intel’s, but at a cheaper price.
Both Intel and AMD produce what we call x86 processors.
So finally, the comparaison should be between the two architectures : x86 and ARM
Differences
X86 & ARM
X86
X86 is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures[a] initially developed by Intel based on the Intel 8086 microprocessor.
ARM
ARM is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments.
Processors designed by different companies may adopt the same ISA(Instruction Set Architecture); for example, both AMD and Intel CPUs are based on the x86 architecture, which means any operating system or program that can run on an Intel CPU can also run on an AMD CPU.
CISC & RISC
CISC
The CISC Stands for Complex Instruction Set Computer, developed by the Intel. It has a large collection of complex instructions that range from simple to very complex and specialized in the assembly language level, which takes a long time to execute the instructions
RISC
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computer Processor, a microprocessor architecture with a simple collection and highly customized set of instructions. It is built to minimize the instruction execution time by optimizing and limiting the number of instructions.
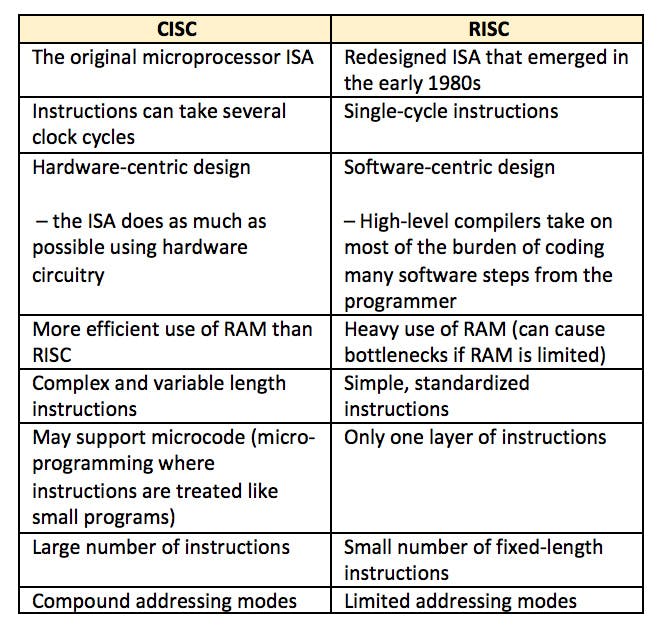
*ISA : Instruction Set Architecture
ARM : smartphones and computers
Arm processors are incredibly energy-efficient and generate less heat. This is crucial for mobile devices such as smartphones, since battery life cannot be too limited, and the device must not get too hot! Arm CPUs are the leading smartphone processor IP on the market today. 95 percent of premium smartphones are powered by Arm.
Arm is also used in many Chromebook laptops, and Apple now offers a number of computers that use the Arm-based M1 chip (before they used Intel x86 chips).
Apple's new MacBook Pro systems, which use the chip, have set a new industry standard for laptop performance and battery life.
The Arm processor is also moving into the server market but more slowly.
Conclusion
Now you know that there are two different types of architectures, x86 and arm.
The way they work are different and the apps developed for one ISA cannot work on the other one.
That's why, when you get a Macbook M1 (or a Chromebook), you have to adjust and download arm-compatible apps.
Don't hesitate to point out some mistakes i've made in the comments, i'm still digging the subject and i wanted to simplify a lot these concepts so maybe i took some shortcuts.

